Botfly infestation in dogs is a concerning issue for pet owners worldwide, causing discomfort and potential health risks if not addressed promptly. This parasitic infection, caused by the Cuterebra species in North America or Dermatobia hominis in other regions, requires awareness and proactive measures to protect your furry friend. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about botflies in dogs, including symptoms, prevention, and treatment options.
As a responsible pet owner, it's essential to stay informed about common health challenges your dog might face. Botflies are one such concern that demands attention due to their lifecycle and impact on canine health. By understanding how these parasites operate and the steps to prevent them, you can ensure your dog remains safe and healthy.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of botflies, covering their biology, signs of infestation, and effective management strategies. Whether you're a seasoned pet owner or new to dog care, the information provided here will equip you with the knowledge needed to safeguard your pet against this parasitic threat.
Read also:Xfinity Outage Understanding Causes Solutions And Staying Connected
Table of Contents
- What is Botfly?
- Life Cycle of Botflies
- Signs and Symptoms of Botfly Infestation
- Prevention Methods for Botfly in Dogs
- Treatment Options for Botfly Infestation
- Biological Impact on Dogs
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Expert Advice on Botfly Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is Botfly?
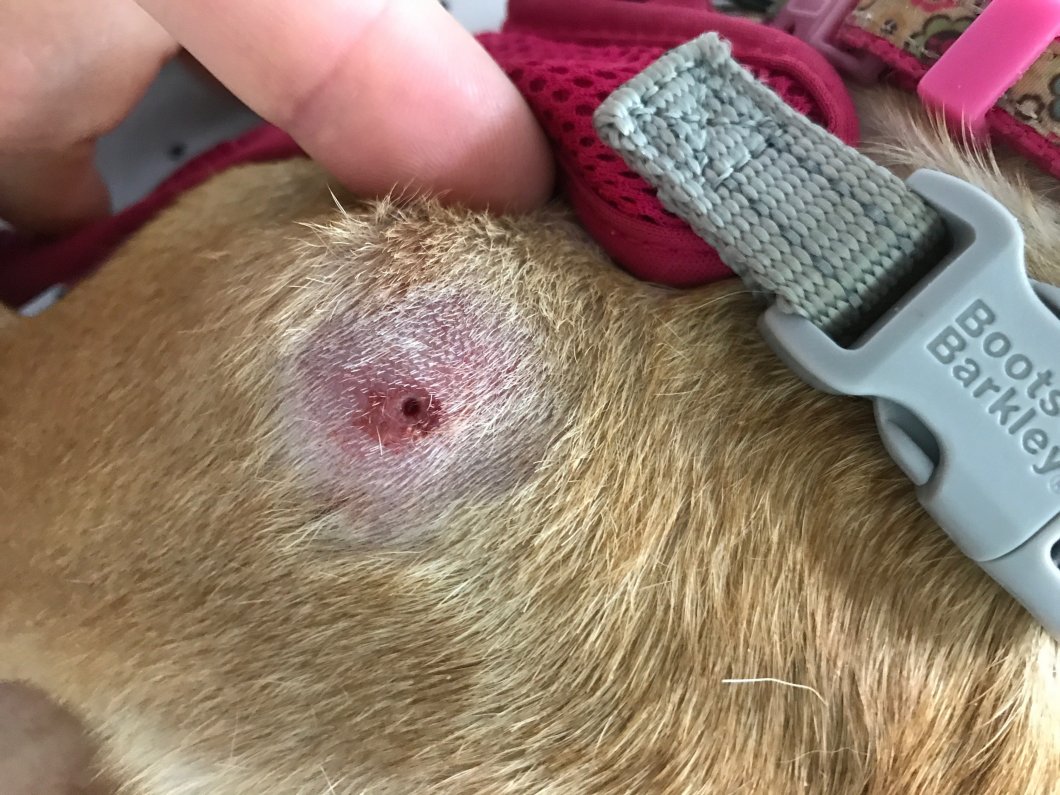
Botflies are parasitic insects that lay eggs near or on the skin of animals, including dogs. The larvae, commonly referred to as "warbles," burrow into the host's tissue, causing irritation and potential infections. While botflies are most prevalent in rural or wooded areas, any dog can be at risk, especially during warmer months.
Types of Botflies Affecting Dogs
There are two primary types of botflies affecting dogs:
- Cuterebra: Native to North America, this species primarily targets small mammals but can also infest dogs.
- Dermatobia hominis: Found in Central and South America, this botfly is known for its aggressive egg-laying behavior and can cause severe infestations.
Life Cycle of Botflies
Understanding the life cycle of botflies is crucial for prevention and management. The process involves several stages:
1. Egg-Laying Stage
Female botflies lay eggs on surfaces where hosts are likely to come into contact, such as grass, leaves, or even your dog's fur. Once the eggs hatch, larvae seek out a host to burrow into.
2. Larval Stage
The larvae penetrate the host's skin, creating a breathing hole as they grow. During this stage, they feed on the host's tissue, causing discomfort and potential infections.
3. Pupal Stage
After maturation, the larvae exit the host and fall to the ground, forming a pupa. This stage lasts several weeks before the adult botfly emerges.
Read also:Nick Sortor The Visionary Entrepreneur Redefining Modern Business
Signs and Symptoms of Botfly Infestation
Recognizing the signs of botfly infestation is vital for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Swollen lumps or bumps under the skin
- A small hole with a visible breathing opening
- Redness, swelling, or pus around the affected area
- Excessive licking or scratching at the site
- Behavioral changes, such as restlessness or irritability
Prevention Methods for Botfly in Dogs
Preventing botfly infestations involves a combination of environmental management and proactive care:
1. Regular Grooming
Regularly inspect your dog's coat for signs of botfly larvae or eggs. Grooming not only helps detect issues early but also strengthens the bond between you and your pet.
2. Avoiding High-Risk Areas
Keep your dog away from wooded or grassy areas during peak botfly seasons. If exposure is unavoidable, ensure your pet is thoroughly checked afterward.
3. Using Preventive Medications
Consult your veterinarian about preventive medications or topical treatments designed to repel botflies and other parasites.
Treatment Options for Botfly Infestation
If your dog is infested with botflies, prompt treatment is essential. The following steps are recommended:
1. Professional Removal
Do not attempt to remove the larvae yourself, as improper extraction can lead to complications. A veterinarian will carefully extract the larvae and clean the wound to prevent infection.
2. Antibiotics and Pain Management
After removal, your vet may prescribe antibiotics to prevent secondary infections and pain medication to ensure your dog's comfort.
3. Monitoring Recovery
Follow up with your veterinarian to ensure proper healing and address any lingering issues.
Biological Impact on Dogs
Botfly infestations can have significant biological effects on dogs, including:
- Localized infections and abscesses
- Systemic infections if larvae migrate internally
- Chronic pain and discomfort
- Impact on overall health and immune function
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mismanagement of botfly infestations can worsen the condition. Avoid the following mistakes:
- Attempting to squeeze or puncture the lump
- Using unapproved home remedies
- Delaying veterinary care
Expert Advice on Botfly Management
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), botflies pose a significant health risk to animals and humans alike. Veterinary experts recommend a proactive approach, combining preventive measures with regular check-ups to ensure your dog remains botfly-free.
Key Recommendations
Stay informed about botfly activity in your area and consult with your veterinarian for region-specific advice. Early detection and treatment are critical for successful management.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can botflies infest humans?
Yes, while rare, botflies can infest humans, particularly Dermatobia hominis. Immediate medical attention is advised if you suspect an infestation.
2. Are certain breeds more susceptible?
No specific breed is more prone to botfly infestations, but outdoor dogs in high-risk areas are at greater risk.
3. How long does recovery take?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the infestation and individual healing rates, but most dogs recover fully within a few weeks.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Botfly infestations in dogs are a serious concern that requires vigilance and prompt action. By understanding the lifecycle, recognizing symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, you can protect your beloved pet from this parasitic threat. Remember, early detection and professional treatment are key to ensuring your dog's health and well-being.
We encourage you to share this article with fellow pet owners and leave a comment below if you have any questions or experiences to share. For more informative content on pet health, explore our other articles and stay connected with our community.
Data Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention