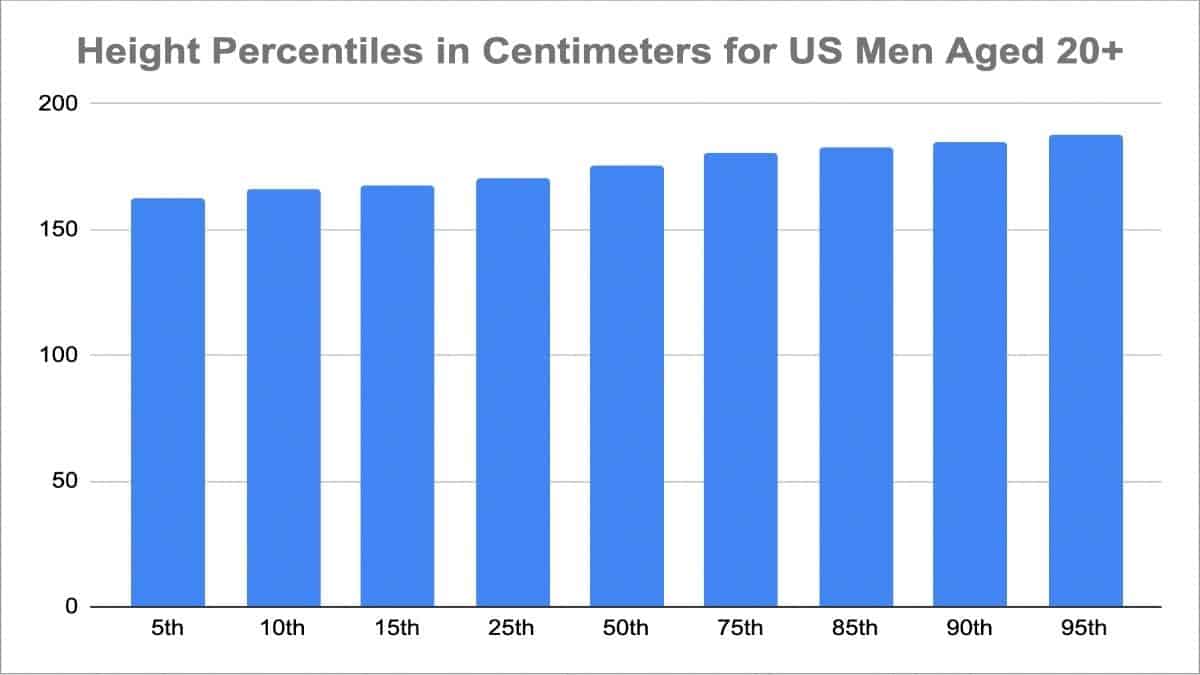
Understanding the average male height is an intriguing topic that bridges science, culture, and health. It reflects biological and environmental factors that shape human growth and development. The global average male height varies significantly across regions, influenced by genetics, nutrition, and lifestyle. If you're curious about how height is measured, what the global trends are, and how it impacts health and well-being, this article is for you.
Height is more than just a physical attribute; it's a reflection of overall health and living conditions. Over the years, researchers have studied height trends to understand how societal changes affect human growth. This article explores the global average male height, its variations across continents, and the factors that contribute to height differences.
Whether you're a student, a health enthusiast, or simply curious about human biology, this comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into male height statistics, contributing factors, and future projections. Let's dive into the world of height and uncover the fascinating details behind the numbers.
Read also:Poppi Monroe A Rising Star In The Spotlight
Table of Contents
- Global Trends in Male Height
- Genetic Factors Affecting Male Height
- The Impact of Nutrition on Male Height
- Environmental Factors Influencing Male Height
- Regional Differences in Average Male Height
- Health Implications of Male Height
- Methods of Measuring Male Height
- A Historical Perspective on Male Height
- Future Projections for Male Height
- Conclusion: What You Need to Know About Male Height
Global Trends in Male Height
The average male height varies significantly across the globe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global average male height is approximately 171 cm (5'7"). However, this figure fluctuates depending on the region, country, and population group. Countries in Northern Europe, such as the Netherlands and Norway, boast some of the tallest men, with averages exceeding 180 cm (5'11").
In contrast, regions like South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa report lower average heights, often below 165 cm (5'5"). These disparities are influenced by a combination of genetic predispositions, socioeconomic conditions, and access to healthcare. Understanding these trends provides valuable insights into global health and development.
Factors Driving Global Height Differences
- Genetic diversity among populations
- Economic development and access to resources
- Cultural practices and dietary habits
Genetic Factors Affecting Male Height
Genetics plays a crucial role in determining an individual's height. Studies suggest that approximately 60-80% of height variation is attributed to genetic factors. Specific genes, such as those involved in bone growth and development, influence how tall a person can grow. However, the genetic contribution to height is complex, involving multiple genes and interactions.
While genetics sets the potential for height, environmental factors often determine whether an individual reaches their full genetic potential. For example, malnutrition during childhood can hinder growth, even if a person has a genetic predisposition for tall stature.
Key Genetic Components
- Genes responsible for bone density and length
- Interactions between genetic variants
- Hereditary patterns within families
The Impact of Nutrition on Male Height
Nutrition is a critical determinant of height, especially during critical growth periods such as infancy, childhood, and adolescence. Adequate intake of essential nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals, supports healthy bone development and overall growth. Malnutrition, particularly during these stages, can result in stunted growth and lower adult height.
Research indicates that improvements in nutrition have contributed to increasing average heights in many parts of the world. For instance, countries that have implemented nutrition programs for children and pregnant women have seen significant increases in average male height over the past few decades.
Read also:How Old Is Puff Daddy A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Career And Legacy
Nutrients Essential for Height Growth
- Protein for muscle and bone development
- Calcium and vitamin D for bone health
- Iron for oxygen transport and energy production
Environmental Factors Influencing Male Height
Environmental factors, such as living conditions, pollution levels, and access to healthcare, also impact male height. Children growing up in clean, safe environments with access to medical care are more likely to achieve their full growth potential. Conversely, exposure to pollutants, stress, and inadequate healthcare can hinder growth and development.
Climate and geography may also play a role. For example, populations living at high altitudes may experience slightly shorter average heights due to reduced oxygen levels. Similarly, extreme temperatures can influence growth patterns, although these effects are generally less pronounced than those of nutrition and healthcare.
Key Environmental Influences
- Living conditions and sanitation
- Exposure to environmental pollutants
- Access to healthcare and medical services
Regional Differences in Average Male Height
Regional variations in average male height highlight the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and socioeconomic factors. In Europe, countries like the Netherlands and Iceland consistently rank among the tallest, with average heights exceeding 180 cm. In contrast, regions such as South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa report lower averages, often below 165 cm.
These differences are not solely due to genetics. Historical factors, such as colonization, economic development, and cultural practices, have shaped regional height trends. For example, countries with strong social safety nets and universal healthcare systems tend to have taller populations, reflecting the importance of societal support in fostering healthy growth.
Regional Height Comparisons
- Europe: Average height > 175 cm
- Asia: Average height 165-170 cm
- Africa: Average height
Health Implications of Male Height
Height is not just a physical characteristic; it also has implications for health and well-being. Studies have shown that taller individuals tend to have lower risks of certain health conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes. However, they may face higher risks of other conditions, such as certain cancers. These associations are likely due to a combination of genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors.
It's important to note that height is only one of many factors influencing health. Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and good mental health are crucial for overall well-being, regardless of height.
Health Risks and Benefits by Height
- Lower risk of heart disease for taller individuals
- Higher risk of certain cancers for taller individuals
- Importance of lifestyle factors in mitigating health risks
Methods of Measuring Male Height
Accurate measurement of height is essential for research, healthcare, and population studies. The most common method involves using a stadiometer, a device designed to measure height with precision. Measurements are typically taken with the individual standing barefoot, with their back against the device and their heels together.
Technological advancements have introduced new methods, such as ultrasonic height measurement devices, which provide quick and accurate readings. However, traditional stadiometers remain the gold standard for clinical and research purposes.
Best Practices for Height Measurement
- Use a calibrated stadiometer for accuracy
- Ensure proper posture during measurement
- Repeat measurements to confirm consistency
A Historical Perspective on Male Height
Historical records provide valuable insights into how average male height has changed over time. For example, archaeological evidence suggests that ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Greeks, had relatively short average heights compared to modern populations. This trend began to change during the industrial revolution, as improvements in nutrition and healthcare led to significant increases in height.
However, historical height trends also reflect periods of decline, such as during wartime or economic depressions, when access to resources was limited. Understanding these patterns helps researchers predict future trends and develop strategies to support healthy growth.
Future Projections for Male Height
Looking ahead, projections suggest that average male height will continue to increase in many parts of the world, driven by improvements in nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. However, the rate of increase may slow in regions where height has already reached its genetic potential, such as Northern Europe.
Global challenges, such as climate change and resource scarcity, may also influence future height trends. Ensuring equitable access to resources and healthcare will be crucial in supporting healthy growth for all populations.
Conclusion: What You Need to Know About Male Height
In conclusion, the average male height is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and socioeconomic factors. Global trends show significant variations across regions, reflecting differences in living conditions and access to resources. Understanding these factors is essential for promoting healthy growth and development worldwide.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, consider sharing it with others who may benefit from the insights. For more in-depth information on health and wellness, explore our other articles and resources.