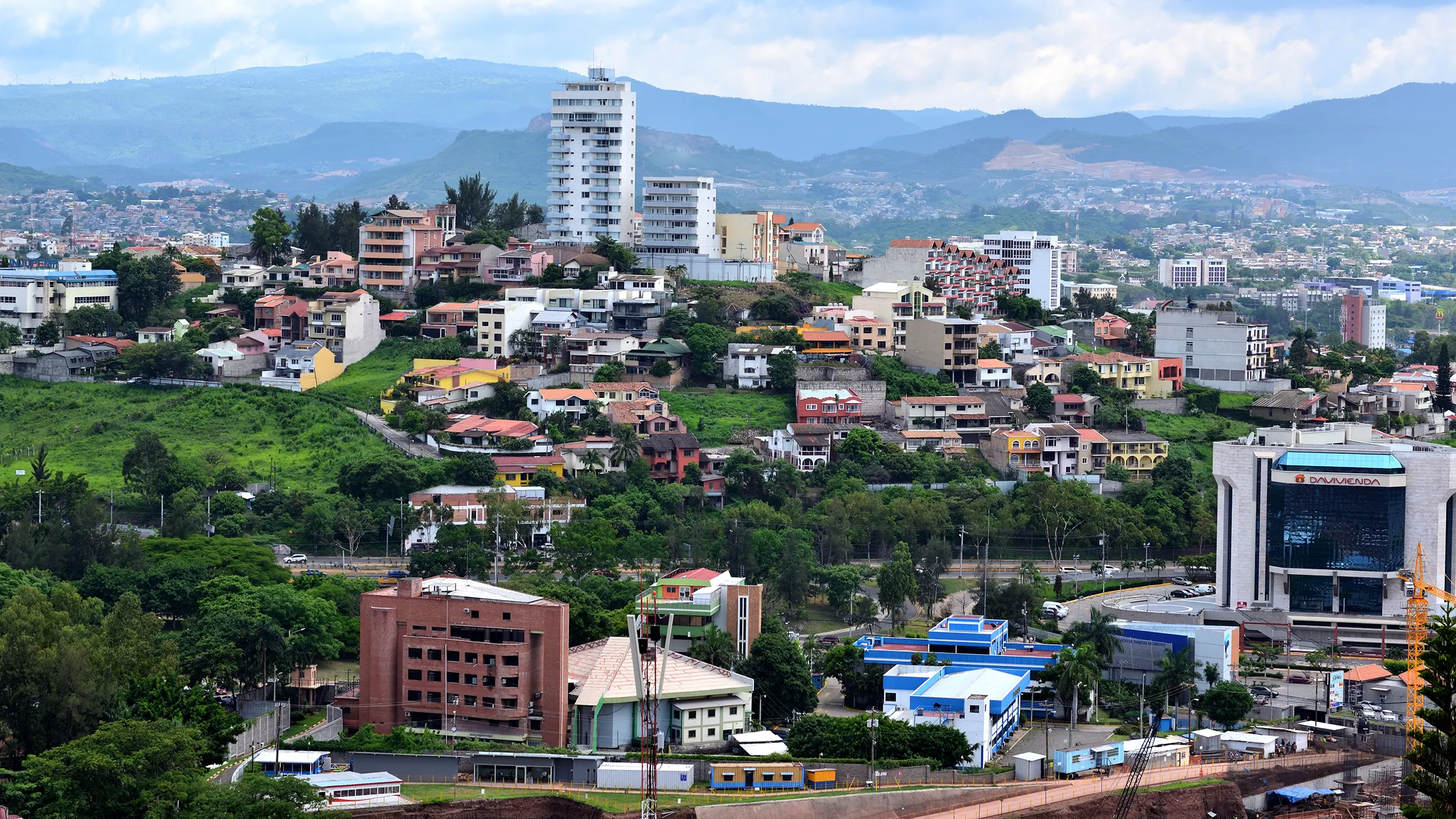
Honduras capital, Tegucigalpa, serves as the political, economic, and cultural hub of this Central American country. As one of the most significant cities in the region, it plays a crucial role in shaping the nation's identity and development. In this article, we'll delve into the history, culture, and significance of Honduras' capital, providing a comprehensive overview of its importance to the country and the wider region.
Tegucigalpa, the capital of Honduras, is not just a city but a testament to the nation's rich history and vibrant culture. Established in the 16th century, it has evolved from a small mining town into a bustling metropolis that reflects the complexities and opportunities of modern Honduras. Whether you're a traveler, a history enthusiast, or simply curious about Central America, understanding Tegucigalpa is essential to grasping the essence of Honduras.
As we explore the Honduran capital, we'll uncover its historical milestones, cultural landmarks, economic contributions, and the challenges it faces in the contemporary world. This article aims to provide a detailed and insightful look into Tegucigalpa, ensuring you gain a well-rounded understanding of its significance in the Central American landscape.
Read also:Baruch College Academic Calendar Your Ultimate Guide For The Academic Year
Table of Contents
- History of Honduras Capital
- Geography and Climate
- Cultural Heritage of Tegucigalpa
- Economic Role of the Honduran Capital
- Political Significance
- Tourism in Tegucigalpa
- Education and Research
- Infrastructure Development
- Challenges Facing the Capital
- Future Prospects
History of Honduras Capital
Founding and Early Years
Tegucigalpa was founded in 1578 by Spanish settlers as a mining town. Its name is derived from the Nahuatl language, meaning "mountain of silver," reflecting its origins as a hub for silver extraction. Over the centuries, the city grew in importance, becoming the administrative center of the Spanish colonial province of Honduras.
By the 19th century, Tegucigalpa had established itself as a key player in the political landscape of the newly independent nation. In 1880, it officially became the capital of Honduras, marking the beginning of its transformation into a modern city.
Geography and Climate
Natural Setting and Weather Patterns
Located in the central part of Honduras, Tegucigalpa is surrounded by picturesque mountains, which contribute to its stunning natural beauty. The city's geography includes valleys and hills, creating a unique urban landscape. Its elevation of approximately 1,000 meters above sea level results in a temperate climate, with warm days and cooler nights.
Residents of the Honduran capital experience distinct wet and dry seasons, with rainfall peaking during the months of May to October. This climate supports a diverse range of flora and fauna, making the city an attractive destination for nature lovers.
Cultural Heritage of Tegucigalpa
Art, Music, and Festivals
Tegucigalpa is a melting pot of indigenous, African, and European influences, reflected in its vibrant cultural scene. The city is home to numerous museums, art galleries, and theaters, offering residents and visitors a glimpse into the rich artistic traditions of Honduras.
Music plays a central role in the cultural life of the capital, with traditional genres like punta and marimba coexisting alongside modern styles. Annual festivals, such as the Feria de San Miguel, celebrate the city's heritage and bring communities together in a spirit of joy and unity.
Read also:Emmitt Smith Iv The Rising Star In The World Of Sports
Economic Role of the Honduran Capital
Key Industries and Economic Drivers
As the economic heart of Honduras, Tegucigalpa contributes significantly to the national GDP. The city hosts a variety of industries, including manufacturing, finance, and services. The textile and garment sector, in particular, has been a major employer and export generator for the region.
Recent years have seen growth in the technology and digital sectors, as Tegucigalpa positions itself as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship. This diversification of the economy promises to enhance the city's resilience and long-term prosperity.
Political Significance
Government and Administration
Tegucigalpa serves as the seat of the Honduran government, housing key institutions such as the National Congress and the Supreme Court. As the political capital, it plays a pivotal role in shaping the nation's policies and governance.
The city's political landscape is dynamic, with various parties and interest groups vying for influence. Civic engagement and public participation are encouraged, fostering a democratic culture that is central to the nation's identity.
Tourism in Tegucigalpa
Attractions and Activities
Tourists visiting Tegucigalpa are treated to a wealth of attractions that showcase the city's history, culture, and natural beauty. The National Museum of Anthropology provides insights into the pre-Columbian civilizations that once thrived in the region, while the Metropolitan Cathedral offers a glimpse into the city's religious heritage.
- Explore the historic Comayagüela district
- Visit the stunning Lake Yojoa
- Experience the vibrant markets of Tegucigalpa
For outdoor enthusiasts, the surrounding mountains and national parks provide opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, and adventure sports.
Education and Research
Universities and Academic Institutions
Tegucigalpa is home to several prestigious universities and research institutions, including the National Autonomous University of Honduras (UNAH). These institutions play a crucial role in educating the nation's future leaders and fostering innovation.
Collaborations with international partners have enhanced the quality of education and research in the city, ensuring that Tegucigalpa remains at the forefront of academic excellence in Central America.
Infrastructure Development
Transportation and Urban Planning
In recent years, significant investments have been made in improving the infrastructure of Tegucigalpa. The expansion of the Toncontín International Airport and the development of modern road networks have enhanced connectivity within the city and beyond.
Efforts are ongoing to improve public transportation and promote sustainable urban planning, addressing the challenges posed by rapid urbanization and population growth.
Challenges Facing the Capital
Social and Economic Issues
Despite its many achievements, Tegucigalpa faces several challenges that require attention and action. Issues such as poverty, inequality, and crime continue to affect the quality of life for many residents. The city's authorities are working closely with local and international organizations to implement programs aimed at addressing these concerns.
Environmental sustainability is another area of focus, as the city seeks to balance development with the preservation of its natural resources.
Future Prospects
Opportunities for Growth and Development
The future of Tegucigalpa looks promising, with numerous opportunities for growth and development on the horizon. Investments in technology, education, and infrastructure are expected to drive economic progress and enhance the city's global competitiveness.
As the Honduran capital continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of Central America. By addressing its challenges and leveraging its strengths, Tegucigalpa is poised to become a model of sustainable urban development.
Conclusion
In summary, Tegucigalpa, the capital of Honduras, is a city of immense historical, cultural, and economic significance. From its humble beginnings as a mining town to its current status as a dynamic metropolis, the city has undergone remarkable transformations. Understanding the Honduran capital provides valuable insights into the nation's past, present, and future.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences about Tegucigalpa in the comments below. For more articles on Central America and beyond, explore our website and stay informed about the world around you.
Data Sources:
- World Bank
- UNESCO
- Honduran National Institute of Statistics