Tuberculosis (TB) skin tests are essential in diagnosing latent TB infection and ensuring early detection of the disease. A positive TB skin test is a critical indicator that someone may have been exposed to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. Understanding how to interpret these tests and what positive TB skin test images look like can help individuals take appropriate steps toward treatment and prevention. This article dives deep into everything you need to know about positive TB skin tests and provides valuable insights for better health management.
Whether you're a healthcare professional, student, or someone concerned about TB diagnosis, this guide is tailored to provide clarity and actionable information. From understanding the basics of TB skin tests to interpreting results, we cover it all. Stay informed and empowered to make the right decisions for your health.
Our goal is to ensure that you have access to accurate and reliable information about positive TB skin test images, helping you navigate the complexities of tuberculosis diagnosis with confidence. Let's get started.
Read also:Eric Greenspan The Culinary Innovator Revolutionizing The Food Industry
What is a TB Skin Test?
A TB skin test, also known as a tuberculin skin test (TST) or Mantoux test, is a diagnostic tool used to determine if someone has been infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. The test involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin purified protein derivative (PPD) just beneath the skin on the forearm. After 48 to 72 hours, a healthcare professional examines the injection site for any reaction.
How is the TB Skin Test Performed?
The process of administering a TB skin test is straightforward:
- A healthcare provider cleans the forearm with alcohol.
- A small needle is used to inject PPD under the skin.
- A small bump, or wheal, forms at the injection site.
- The patient must return within 48 to 72 hours for the healthcare provider to evaluate the test results.
It's crucial to follow up within the specified timeframe to ensure accurate results.
Why is the TB Skin Test Important?
The TB skin test plays a vital role in public health:
- It helps identify individuals who may have latent TB infection.
- Early detection can prevent the progression to active TB disease.
- It aids in controlling the spread of tuberculosis in communities.
Understanding the significance of this test is key to managing TB effectively.
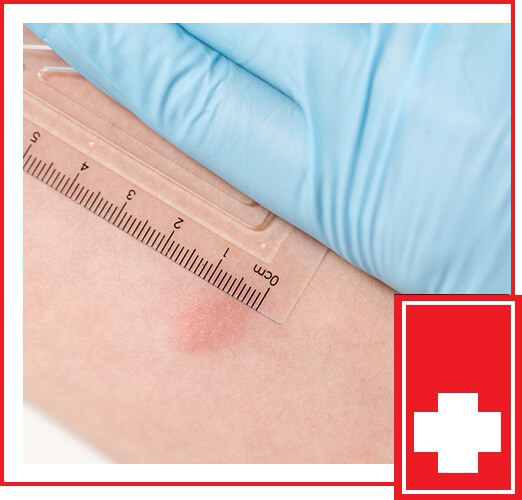
Positive TB Skin Test Images
Positive TB skin test images are visual representations of the reaction that occurs at the injection site when someone has been exposed to TB bacteria. These images help healthcare providers and patients understand what to look for when interpreting test results.
Read also:Xfinity Outage Understanding Causes Solutions And Staying Connected
What Does a Positive TB Skin Test Look Like?
A positive TB skin test typically shows the following characteristics:
- A raised, hard swelling at the injection site.
- The swelling is measured in millimeters using a ruler.
- Redness alone does not necessarily indicate a positive result unless accompanied by swelling.
Referencing positive TB skin test images can assist in identifying these signs more accurately.
Interpreting Positive TB Skin Test Results
The interpretation of a positive TB skin test depends on various factors, including the size of the swelling and the individual's risk factors. Here are some guidelines:
- For individuals with no known risk factors, a swelling of 15 mm or more is considered positive.
- For those with moderate risk factors, a swelling of 10 mm or more indicates a positive result.
- For high-risk individuals, such as those with HIV or close TB contacts, a swelling of 5 mm or more is considered positive.
These criteria are based on established medical guidelines and should be followed closely.
Understanding TB Infection
Tuberculosis infection can manifest in two forms: latent TB infection and active TB disease. A positive TB skin test indicates exposure to TB bacteria but does not necessarily mean the individual has active TB.
Latent TB Infection vs. Active TB Disease
Here’s a breakdown of the differences:
- Latent TB Infection: The bacteria are present in the body but are not actively multiplying. Individuals with latent TB are not contagious and do not exhibit symptoms.
- Active TB Disease: The bacteria are multiplying and causing symptoms such as coughing, fever, and weight loss. Active TB is contagious and requires immediate treatment.
Recognizing the distinction between these two forms is crucial for appropriate management.
Risk Factors for TB Infection
Certain groups are at higher risk of developing TB infection:
- People living in or traveling to areas with high TB prevalence.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
- Close contacts of people with active TB disease.
Being aware of these risk factors can help prioritize testing and treatment.
Diagnosing TB Infection
Diagnosing TB infection involves a combination of tests, including the TB skin test and interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs). Each method has its advantages and limitations.
Advantages of the TB Skin Test
The TB skin test offers several benefits:
- It is widely available and relatively inexpensive.
- It does not require specialized equipment or laboratory facilities.
- It provides results within 48 to 72 hours.
Despite these advantages, it's important to consider its limitations as well.
Limitations of the TB Skin Test
Some drawbacks of the TB skin test include:
- False-positive results may occur due to prior BCG vaccination or exposure to non-tuberculous mycobacteria.
- False-negative results can happen in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- The test requires a follow-up visit for interpretation, which may not always be feasible for some patients.
Understanding these limitations can help in selecting the most appropriate diagnostic tool for each individual.
Treatment for Positive TB Skin Test
Individuals with a positive TB skin test may require treatment, especially if they have latent TB infection. Treatment aims to eliminate the bacteria and prevent the development of active TB disease.
Medications for Latent TB Infection
The most common medications used to treat latent TB infection include:
- Isoniazid (INH): Taken daily for 9 months.
- Rifampin: Taken daily for 4 months.
- Combination therapy: Sometimes prescribed for shorter treatment durations.
Adherence to the prescribed regimen is critical for successful treatment.
Side Effects of TB Medications
While TB medications are generally safe, they can cause side effects in some individuals:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Rash or itching.
Patients should report any adverse effects to their healthcare provider immediately.
Preventing TB Infection
Prevention is key to controlling the spread of tuberculosis. Several strategies can help reduce the risk of TB infection:
Vaccination with BCG
The Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine is used in many countries to protect against TB. However, its effectiveness varies, and it may not prevent all forms of TB.
Practicing Good Hygiene
Simple practices can make a big difference:
- Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Washing hands frequently.
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have active TB disease.
These measures can help minimize the risk of transmission.
Positive TB Skin Test Images and Resources
Accessing high-quality positive TB skin test images and resources can enhance understanding and improve diagnostic accuracy. Here are some trusted sources:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
The CDC provides comprehensive information on TB skin tests, including visual aids and guidelines for interpretation.
World Health Organization (WHO)
The WHO offers global resources and recommendations for TB diagnosis and management, ensuring that healthcare providers and patients have access to the latest information.
Referencing these sources can help ensure that you are working with the most up-to-date and reliable data.
Frequently Asked Questions About Positive TB Skin Tests
What Happens if My TB Skin Test is Positive?
A positive TB skin test means you have been exposed to TB bacteria. Your healthcare provider will likely recommend further testing, such as a chest X-ray or sputum test, to determine if you have active TB disease.
Can a Positive TB Skin Test Be Wrong?
Yes, false-positive results can occur due to factors like prior BCG vaccination or exposure to non-tuberculous mycobacteria. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your individual risk factors to determine the likelihood of a true positive result.
How Long Does It Take for TB Test Results?
Results of a TB skin test are typically available within 48 to 72 hours after the test is administered.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding positive TB skin test images and the diagnostic process is essential for effective TB management. From recognizing the signs of a positive test to exploring treatment options and prevention strategies, this guide provides comprehensive information to empower individuals and healthcare providers alike.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. For further reading, explore our other articles on health and wellness topics. Together, we can work toward a healthier future and a world free of tuberculosis.
Table of Contents