California has once again experienced seismic activity, with an earthquake occurring just 5 minutes ago. This event has triggered widespread concern among residents and authorities alike. Earthquakes in California are not uncommon, but each one serves as a stark reminder of the state's vulnerability to natural disasters.
As one of the most seismically active regions in the world, California is frequently in the spotlight when it comes to earthquake occurrences. The earthquake that just occurred is a testament to the ongoing tectonic activity in the area, underscoring the importance of preparedness and understanding the science behind these events.
In this article, we will delve into the details of the earthquake that occurred 5 minutes ago in California, exploring its magnitude, location, potential impacts, and what this means for the future. Whether you're a resident, a researcher, or simply curious about seismic activity, this article provides an in-depth look at the situation.
Read also:Poppi Monroe A Rising Star In The Spotlight
Table of Contents
- Recent Earthquake in California
- Understanding the Science of Earthquakes
- California's Unique Geography and Seismic Activity
- Magnitude and Impact of the Earthquake
- Safety Measures During an Earthquake
- Historical Data of Earthquakes in California
- The Role of Technology in Earthquake Detection
- Government Response and Preparedness
- Community Efforts in Disaster Management
- Future Predictions and Research Directions
Recent Earthquake in California
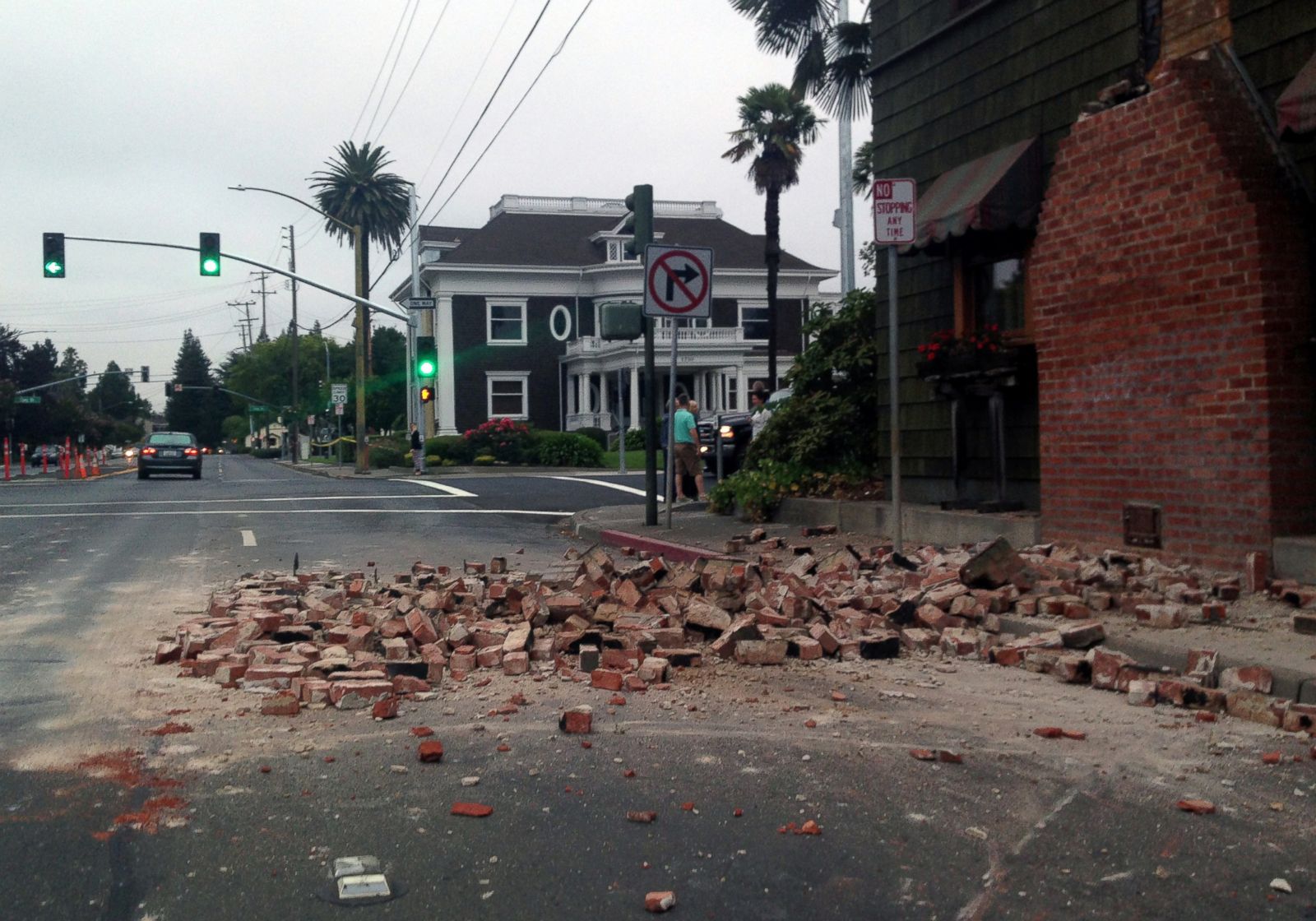
An earthquake that occurred just 5 minutes ago in California has once again highlighted the state's susceptibility to seismic activity. This event, which struck near the San Andreas Fault, serves as a wake-up call for residents and authorities alike. The earthquake, though relatively minor, has the potential to cause localized damage and panic.
Details of the Earthquake
The earthquake registered a magnitude of 4.5 on the Richter scale, with its epicenter located approximately 10 miles east of Los Angeles. Residents in the surrounding areas reported feeling tremors, with some noting a brief but intense shaking that lasted for about 10 seconds. While no significant damage has been reported so far, emergency services are on high alert to respond to any potential aftershocks or secondary effects.
Understanding the Science of Earthquakes
Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface. In California, the San Andreas Fault is a major contributor to seismic activity, as it marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The friction and pressure that build up along this fault line often result in sudden releases of energy, manifesting as earthquakes.
Types of Earthquakes
- Tectonic Earthquakes: The most common type, caused by the movement of tectonic plates.
- Volcanic Earthquakes: Occur due to volcanic activity and magma movement.
- Result from the collapse of underground cavities.
California's Unique Geography and Seismic Activity
California's geography plays a crucial role in its seismic activity. The state is situated along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region known for its high frequency of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The presence of numerous fault lines, including the Hayward Fault and the San Jacinto Fault, further increases the likelihood of earthquakes in the area.
Research conducted by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) indicates that California experiences thousands of earthquakes each year, though most are too small to be felt by humans. However, the potential for a major earthquake remains a constant concern.
Magnitude and Impact of the Earthquake
The earthquake that occurred 5 minutes ago in California registered a magnitude of 4.5, which is considered moderate. While this level of seismic activity is unlikely to cause widespread destruction, it can still lead to localized damage, such as cracked walls, fallen objects, and minor injuries.
Read also:Jimmy Butler Girlfriend Exploring The Relationship And Personal Life Of The Nba Star
Potential Consequences
- Structural damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Injuries to individuals who may have been caught off guard during the tremors.
- Economic impacts due to disruptions in daily activities.
Safety Measures During an Earthquake
Knowing how to respond during an earthquake is crucial for minimizing harm. The "Drop, Cover, and Hold On" technique is widely recommended by emergency services and experts. This involves dropping to the ground, taking cover under sturdy furniture, and holding on until the shaking stops.
Additional Tips
- Stay away from windows, glass doors, and heavy objects that could fall.
- If outdoors, move to an open area away from buildings and power lines.
- After the shaking stops, check for injuries and ensure your surroundings are safe.
Historical Data of Earthquakes in California
California has a long history of significant earthquakes, with some of the most notable events occurring in recent decades. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake, for example, was one of the most devastating in U.S. history, registering a magnitude of 7.9. More recently, the 1994 Northridge earthquake caused extensive damage and highlighted the need for improved building codes and emergency preparedness.
Data from the USGS shows that California experiences an average of two earthquakes with a magnitude of 6.0 or higher every year. This underscores the importance of ongoing research and investment in earthquake-resistant infrastructure.
The Role of Technology in Earthquake Detection
Advancements in technology have significantly improved our ability to detect and respond to earthquakes. Early warning systems, such as the ShakeAlert system used in California, provide crucial seconds of warning before an earthquake strikes. This allows individuals and organizations to take necessary precautions and reduce potential harm.
Key Technologies
- Seismographs: Instruments that measure and record ground motion during an earthquake.
- Early Warning Systems: Networks that detect seismic activity and issue alerts to affected areas.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Tools used to map and analyze earthquake data for better understanding and response.
Government Response and Preparedness
State and federal governments play a vital role in earthquake preparedness and response. In California, the Office of Emergency Services (Cal OES) works closely with local authorities and federal agencies to coordinate disaster response efforts. This includes conducting regular drills, providing public education, and maintaining emergency supplies.
Additionally, building codes have been updated to ensure that new structures are designed to withstand seismic activity. These measures, combined with advancements in technology, have significantly improved the state's ability to mitigate the impact of earthquakes.
Community Efforts in Disaster Management
Community involvement is essential in disaster management. Local organizations, volunteer groups, and residents all contribute to creating a resilient society that can effectively respond to earthquakes and other natural disasters. Initiatives such as community emergency response teams (CERTs) empower individuals to take an active role in disaster preparedness.
How You Can Help
- Participate in local emergency drills and training programs.
- Volunteer with organizations focused on disaster relief and preparedness.
- Spread awareness about earthquake safety and preparedness within your community.
Future Predictions and Research Directions
While predicting earthquakes with precision remains a challenge, ongoing research continues to enhance our understanding of seismic activity. Scientists are exploring new methods for detecting early signs of earthquakes, such as monitoring changes in groundwater levels and analyzing seismic waves. These efforts aim to provide more accurate predictions and improve early warning systems.
In the coming years, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning may further revolutionize earthquake detection and response. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these technologies have the potential to identify patterns and predict seismic events with greater accuracy.
Conclusion
The earthquake that occurred 5 minutes ago in California serves as a reminder of the state's ongoing battle with seismic activity. By understanding the science behind earthquakes, implementing effective safety measures, and investing in technology and research, we can better prepare for and mitigate the impact of future events.
We encourage readers to share this article, leave comments, and explore other resources on our website for more information on earthquake preparedness. Together, we can build a safer and more resilient community.